Symptoms of ingrown hair are physical manifestations of embedded hair shafts within the skin. It usually occurs when a shaved or tweezed hair strand bends and penetrates back into the surrounding dermis.
Recognizing the symptoms of ingrown hair is essential for effective treatment and prevention. They include: sharp pain, redness, itching, swelling, and visible black dots or bumps on the skin.
Early detection and management of ingrown hairs are crucial to avoid infections and scarring. Historically, methods to remove unwanted hair have existed for centuries. However, understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of ingrown hair enables individuals to make informed decisions about hair removal techniques and minimize the risks.
This article will delve into the various symptoms of ingrown hair, their causes, and effective treatment options.
Symptoms of Ingrown Hair
Understanding the symptoms of ingrown hair is crucial for effective management and prevention. These symptoms manifest due to hair shafts penetrating the surrounding skin, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
- Inflammation: Redness, swelling, and pain
- Infection: Pus, drainage, and fever
- Appearance: Black dots or bumps on the skin
- Location: Commonly in areas with coarse hair, such as the beard, pubic area, and underarms
- Risk factors: Shaving, tweezing, or waxing
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the individual and the extent of the ingrown hair. Understanding these aspects helps individuals identify and address ingrown hairs promptly, reducing the risk of complications and promoting skin health.
Inflammation
Inflammation is a common symptom of ingrown hairs and can manifest in various forms. Understanding its components and implications is crucial for effective management and prevention.
- Redness: Redness occurs due to increased blood flow to the affected area, causing the skin to appear red and inflamed.
- Swelling: Swelling is caused by fluid accumulation in the tissues surrounding the ingrown hair, leading to a raised, puffy appearance.
- Pain: Pain is a result of nerve stimulation caused by the ingrown hair irritating the surrounding skin and tissues.
These inflammatory symptoms can range in severity from mild discomfort to severe pain and swelling, depending on the individual's skin sensitivity and the extent of the ingrown hair. Recognizing and promptly addressing inflammation is essential to prevent further complications and promote healing.
Infection
Infection is a severe complication of ingrown hair that requires prompt medical attention. It occurs when bacteria enter the skin through the damaged hair follicle, leading to inflammation and the accumulation of pus and fluids.
The presence of infection significantly amplifies the symptoms of ingrown hair. The affected area becomes more inflamed, painful, and swollen. Additionally, individuals may experience drainage of pus or other fluids from the infected follicle. In severe cases, infection can spread to the surrounding tissues, causing fever, chills, and malaise.
Understanding the connection between infection and ingrown hair is crucial for effective management. Early detection and treatment of ingrown hairs can prevent the onset of infection. Individuals should seek medical attention if they experience any signs of infection, such as persistent pain, swelling, drainage, or fever. Prompt treatment with antibiotics and proper wound care can resolve the infection and minimize the risk of further complications.
Appearance
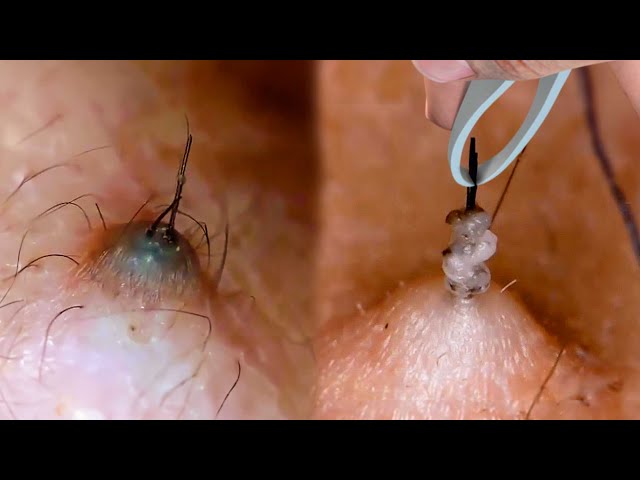
The appearance of black dots or bumps on the skin is a telltale sign of ingrown hair, a common skin condition that occurs when hair shafts curl back and penetrate the surrounding skin. These visible manifestations provide valuable clues for timely identification and effective management.
- Black dots: These are the tips of the embedded hair shafts, which appear as small, dark spots on the skin's surface.
- Bumps: These are raised, inflamed areas that form around the ingrown hair, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and pain.
- Pus-filled bumps: In severe cases, the bumps may become infected, leading to the accumulation of pus and the formation of white or yellow-headed pustules.
- Keloids: In rare instances, ingrown hairs can trigger the formation of keloids, which are raised,that extends beyond the original boundaries of the ingrown hair.
Recognizing the appearance of black dots or bumps on the skin as symptoms of ingrown hair is crucial for prompt intervention. Proper treatment can alleviate discomfort, prevent infection, and minimize the risk of scarring.
Location
The location of ingrown hairs is directly related to the symptoms they cause. Ingrown hairs commonly occur in areas with coarse hair, such as the beard, pubic area, and underarms, due to the thicker and more rigid nature of the hair in these regions. Coarse hair is more likely to curl back and penetrate the skin, leading to inflammation, pain, and other symptoms.
For example, men with coarse beards often experience ingrown hairs after shaving, as the cut hair shafts can easily curl back into the skin. Similarly, individuals who wax or tweeze their pubic hair may develop ingrown hairs due to the removal of the hair from the root, causing it to grow back irregularly. In the underarm area, where hair is typically coarse and grows in multiple directions, ingrown hairs can also be a common problem.
Understanding the connection between ingrown hairs and coarse hair in specific locations is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Individuals can modify their hair removal techniques or use specialized products designed to reduce the risk of ingrown hairs in these areas. By addressing the underlying cause, it becomes possible to minimize the symptoms and discomfort associated with ingrown hairs.
In summary, the location of ingrown hairs in areas with coarse hair, such as the beard, pubic area, and underarms, plays a significant role in determining the symptoms experienced. Understanding this relationship allows for targeted interventions and preventive measures to effectively manage ingrown hairs and maintain healthy skin.
Risk factors
Shaving, tweezing, or waxing are common hair removal methods that can increase the risk of developing ingrown hairs. These techniques involve removing hair from the root, which can cause the hair to grow back irregularly and become trapped under the skin.
When hair is shaved, the sharp edge of the razor can create small nicks or cuts in the skin, allowing bacteria to enter and potentially leading to infection. Tweezing and waxing, on the other hand, remove the entire hair shaft, including the root. This can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle and cause the hair to grow back in an abnormal direction, increasing the likelihood of it becoming ingrown.
For example, men who shave their beards may experience ingrown hairs due to the coarse and curly nature of beard hair. Women who wax their bikini line may also develop ingrown hairs because the hair in this area is often thick and prone to ingrowing. Understanding the connection between hair removal methods and ingrown hairs is essential for individuals to make informed decisions about their hair removal choices and minimize the risk of developing this condition.
In summary, shaving, tweezing, or waxing can increase the risk of ingrown hairs by disrupting the natural hair growth cycle and causing the hair to grow back irregularly. Recognizing this connection can help individuals adjust their hair removal techniques or explore alternative methods to reduce the likelihood of developing ingrown hairs and maintain healthy skin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Ingrown Hair Symptoms
This section addresses common questions and concerns related to the symptoms of ingrown hair. These FAQs aim to provide concise and informative answers to help individuals better understand and manage this condition.
Question 1: What are the typical symptoms of ingrown hair?
Answer: Common symptoms include inflammation (redness, swelling, and pain), infection (pus, drainage), dark spots or bumps on the skin, and itching.
Question 2: Why do I get ingrown hairs?
Answer: Ingrown hairs occur when shaved, tweezed, or waxed hair shafts curl back and penetrate the surrounding skin.
Question 3: Are ingrown hairs contagious?
Answer: No, ingrown hairs are not contagious.
Question 4: How can I prevent ingrown hairs?
Answer: Prevention methods include shaving with a sharp razor, avoiding harsh hair removal techniques, and exfoliating regularly.
Question 5: When should I seek medical attention for ingrown hairs?
Answer: Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, swelling, drainage, or fever, as these may indicate an infection.
Question 6: Are there any long-term effects of ingrown hairs?
Answer: Ingrown hairs can lead to scarring or keloid formation if not treated promptly and properly.
Summary: Understanding the symptoms of ingrown hair is crucial for effective management. Common symptoms include inflammation, infection, and visible skin manifestations. Prevention and early treatment are essential to minimize discomfort and potential complications.
Transition: The following section will delve deeper into the causes and treatment options for ingrown hair, providing additional insights and guidance.
Tips for Managing Ingrown Hair Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of ingrown hair is crucial, but equally important is taking proactive steps to manage and prevent them. This section provides practical tips to help individuals effectively address ingrown hair symptoms and maintain skin health.
Tip 1: Shave with a sharp razor: A dull razor can tug and break hair, increasing the risk of ingrown hairs. Use a sharp razor and replace it regularly.
Tip 2: Avoid harsh hair removal techniques: Tweezing or waxing can remove hair from the root, making it more likely to grow back irregularly and become ingrown. Consider alternative hair removal methods, such as shaving or laser hair removal.
Tip 3: Exfoliate regularly: Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells and allows ingrown hairs to break through the skin's surface. Use a gentle scrub 2-3 times a week.
Tip 4: Apply warm compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help soften the skin and reduce inflammation.
Tip 5: Use over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream: Hydrocortisone cream can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with ingrown hairs.
Tip 6: Avoid tight clothing: Tight clothing can rub against the skin and irritate ingrown hairs, making them more painful and noticeable.
By incorporating these tips into your skincare routine, you can effectively manage ingrown hair symptoms, prevent future occurrences, and maintain healthy, smooth skin.
The following section will discuss additional treatment options for ingrown hairs, including medical interventions and home remedies.
Conclusion
Understanding the symptoms of ingrown hair is vital for effective management and prevention. This article has explored the various symptoms, their causes, and the importance of recognizing them early on. Key points discussed include:
- Ingrown hairs manifest as inflammation, infection, and visible skin changes.
- Shaving, tweezing, and waxing can increase the risk of developing ingrown hairs.
- Prompt treatment and preventive measures are crucial to minimize discomfort and potential complications.
Recognizing the symptoms of ingrown hair empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy skin. By incorporating effective hair removal techniques, exfoliating regularly, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can effectively prevent and manage ingrown hairs. Remember, healthy skin is achievable with proper care and attention.

No comments:
Post a Comment